The Best DIY STEM Tutorials and Projects

OVERVIEW
Have you ever wondered how bats find their way in the dark? They use a special technique called echolocation, which helps them navigate and avoid obstacles. In this blog post, we will explore how an amazing gadget called an ultrasonic distance sensor works in a similar way, using sound waves to measure distances. This fun and simple guide is perfect for kids, parents, and teachers to learn together.

How Ultra Sonic Distance Sensor Works
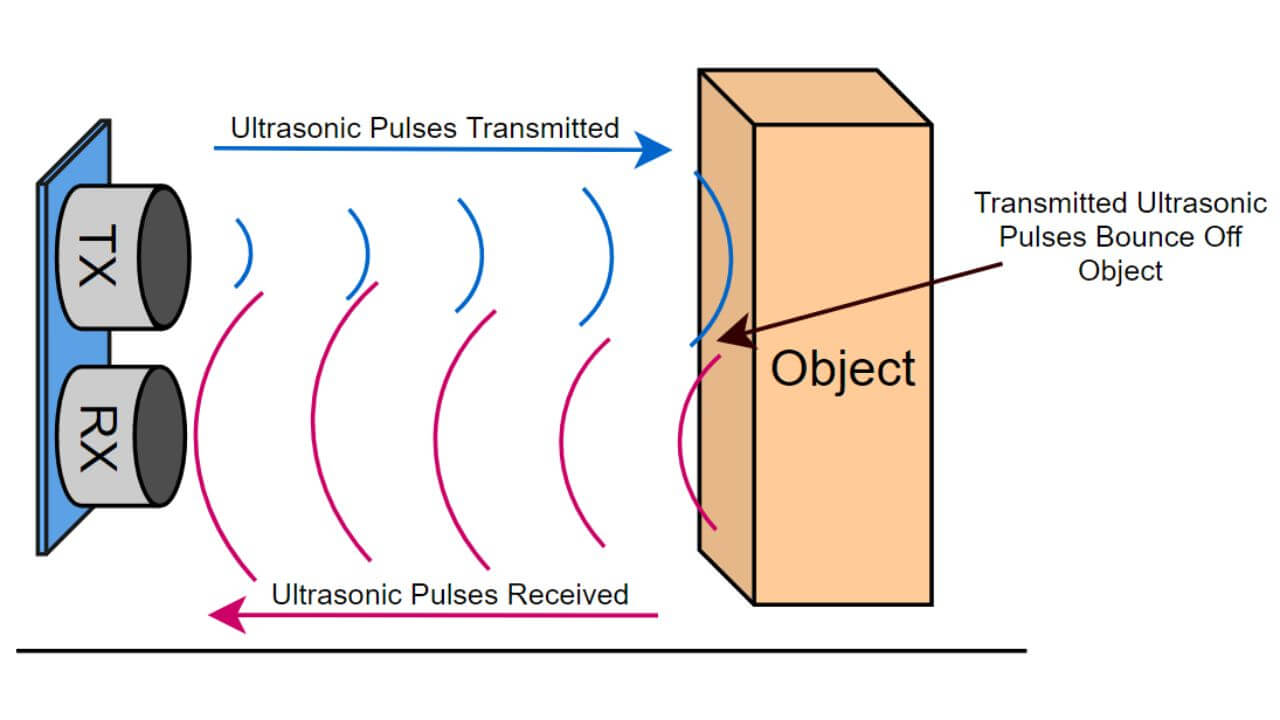
An ultrasonic distance sensor is like a gadget that can measure how far away something is by using sound waves. These sound waves are called “ultrasonic” because they are too high-pitched for our ears to hear. The sensor has two tiny parts called a transmitter and a receiver.
- The transmitter sends out ultrasonic sound waves, which travel through the air like invisible ripples.
- When the sound waves hit an object, they bounce back like an echo towards the sensor.
- The receiver listens for these returning sound waves.
- The sensor measures the time it takes for the sound to travel out and come back, like a stopwatch.
Since we know how fast sound travels approximately 343 meters per second in dry air at room temperature), we can calculate the distance between the sensor and the object using newtons law
S = V x T
in the above formula S = distance, V = Speed of sound = 343 m/s, and T is the time from the sensor.
so this a how the ultrasonic sensor calculates the distance.
Why We Can’t Hear Ultrasonic Sounds
- Human ears can typically hear sounds ranging from 20 to 20,000 Hertz (Hz).
- Ultrasonic sounds have a frequency higher than 20,000 Hz.
- This means ultrasonic sounds are beyond the range of what we can hear.
- The sounds emitted by ultrasonic distance sensors are too high-pitched for humans to hear.
- This is helpful because it prevents the sensor’s sounds from interfering with the sounds we can hear in our daily lives.

Assignment
Find out what is infrasonic Sounds, and tell us the names of 3 animals that can hear ultrasonic sounds and names 3 animals that can hear infrasonic sounds (tell us the answer in the comments)
Real World Examples
Ultrasonic distance sensors are used in many interesting ways. Here are some examples of how they can be applied in real-world situations:
- Robotics: Some robots use ultrasonic sensors to navigate and avoid obstacles, just like bats do. This helps them move around safely without bumping into things.
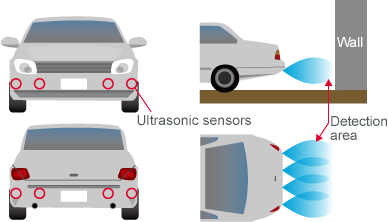
- Parking Assistance: Cars can be equipped with ultrasonic sensors to help drivers park more easily. The sensors detect how close the car is to other objects, like walls or other vehicles, and alert the driver with beeping sounds or visual cues.
- Water Level Monitoring: Ultrasonic sensors can be used to measure the water level in tanks, reservoirs, or rivers. This information helps manage water resources and can alert authorities in case of floods.
- Interactive Exhibits: Museums and science centers sometimes use ultrasonic sensors in interactive exhibits to create fun, hands-on learning experiences. For example, visitors could wave their hands in front of a sensor to control lights, sounds, or images on a screen.
Video
Watch this video to get a better understanding of ultrasonic distance sensors!
Conclusion
Ultrasonic distance sensors are fascinating tools that use sound waves to measure distances, just like bats do with echolocation. With many practical applications, these sensors make our world a smarter and safer place. We hope this fun and simple guide helps kids, parents, and teachers explore the exciting world of ultrasonic distance sensors together while learning about the speed of sound and why we can’t hear ultrasonic sounds.
Happy exploring! Next, We will learn how to use these sensors and make a real-life project using it.!



